How to Choose a Control System for CNC Wood Router?
How to Choose a Control System for CNC Wood Router?
- Jan 29, 2026

As the brain of a CNC Router Machine, the control system is a core component that directly dictates the machine's machining precision, efficiency, operational complexity and applicable scenarios. A suitable control system doubles the results with half the effort in production; otherwise, even a machine with excellent hardware configuration may suffer poor machining performance and low efficiency due to incompatible system matching. This article will detail the pros and cons of mainstream CNC Router control systems and provide scientific selection suggestions based on practical demands.
What Types of CNC Systems Are There for a CNC Router?
The control systems for CNC Router can be broadly classified into three categories by form: PC-based systems, embedded all-in-one control systems, and embedded handheld controller systems.
1. PC-based Systems
This type of system adopts an industrial personal computer (IPC) or commercial PC as the hardware platform, and realizes control by installing CNC software (e.g., Mach3, NcStudio).
🧩 System Architecture
A PC-based CNC system typically consists of four core components:
1.1. PC (Host Computer)
Runs the user interface and core control algorithms.

The PC for CNC router machine
1.2. Control Software
Converts G-code files (.nc, .tap, etc.) generated by CAM software or directly drawn vector graphics into control signals for stepper/servo motors that the machine can execute.
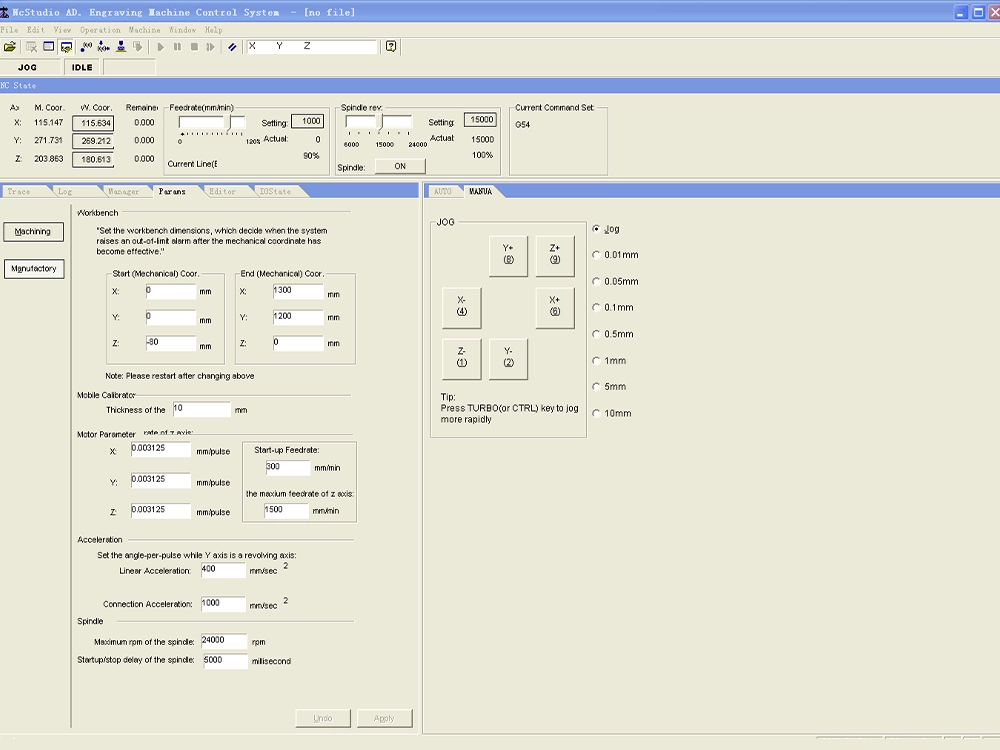
The NcStudio software
1.3. Motion Controller
As the nerve center of the entire system, its core role is to convert the machining instructions from the PC (host computer) into physical signals that can accurately drive motor movement. It serves as a critical bridge connecting the virtual software world and the real mechanical world.
Motion controllers connect to the PC through different interfaces, each with distinct characteristics:
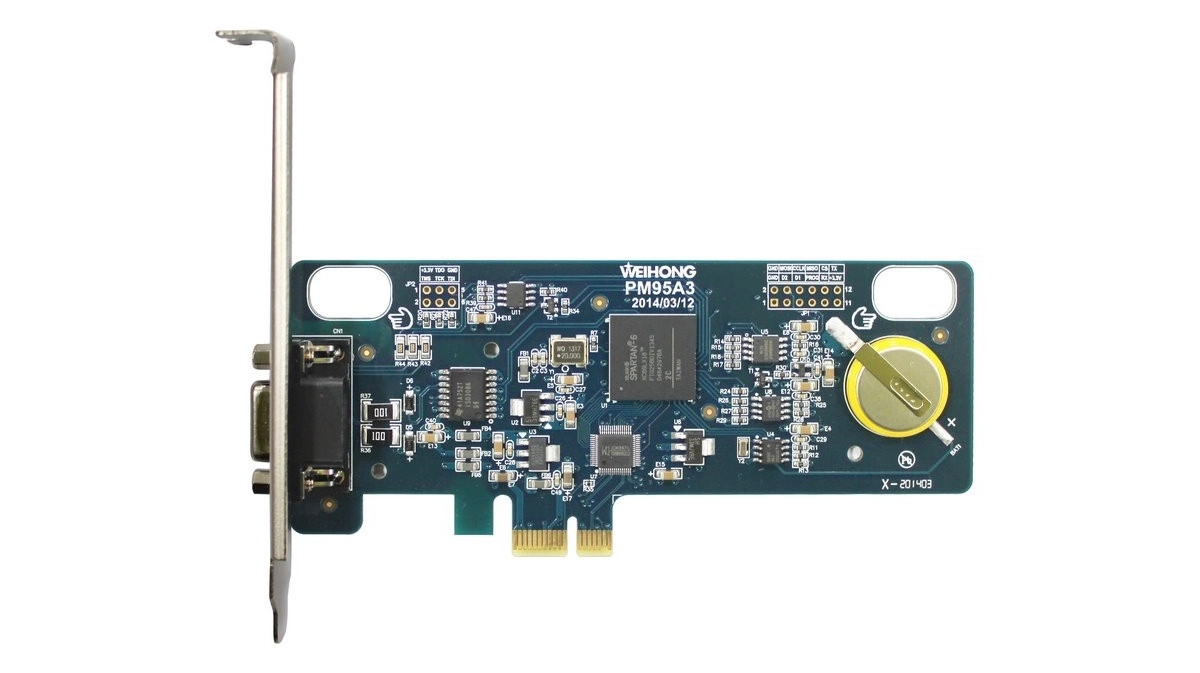
The Weihong PM95A PCIe bus motion control card
Parallel port (LPT)
A classic method in the early days, now obsolete. The software sends pulse signals directly through the parallel port.
PCI/PCIe bus motion control card
The most mainstream method at present. The control card is directly inserted into the PCI or PCIe slot of the PC, featuring high bandwidth, extremely low latency and the most stable communication.
USB motion control card
The PC connects to an external control card via USB, and a dedicated chip on the card processes pulse signals.
Ethernet motion control card
A trend for high-end and industrial-grade applications. Connected via a network, it has extremely strong anti-interference ability, long transmission distance (over 100 meters) and stable connection, making it ideal for multi-machine management and workshop environments.
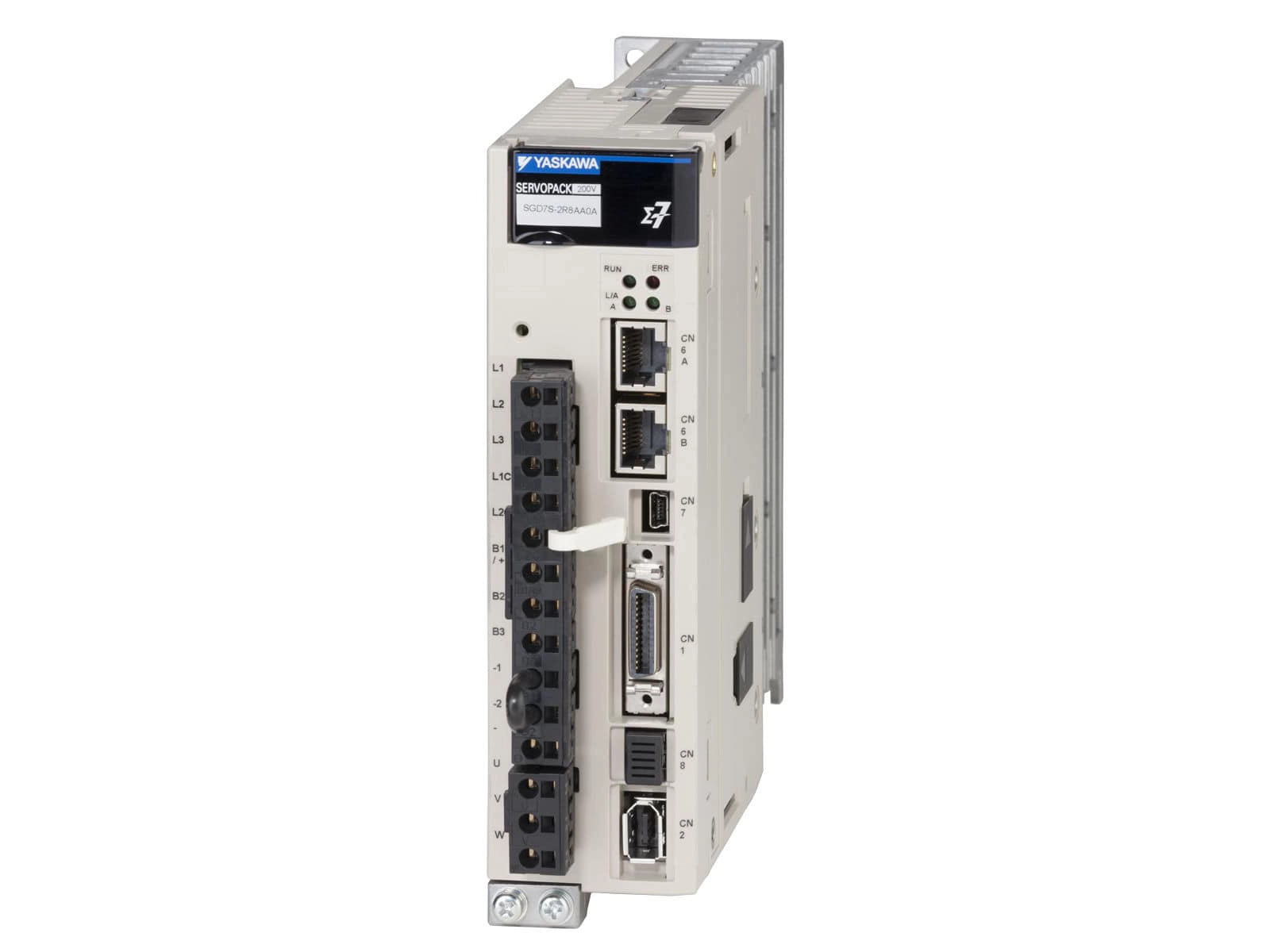
1.4. Slave Controllers, Drivers & Motors (Slave Computer Actuators)
Receive pulse/direction signals from the control card and drive stepper or servo motors for precise rotation.

The Weihong Lambda 3S slave controller

The Yaskawa servo motors and drivers
✅ Advantages
Open Software and Hardware Architecture
- Open software: Users can independently select or replace control software (still requiring adaptation with corresponding control cards) and install various CAM software for design.
- Open hardware: The host computer is usually a standard industrial PC (IPC), whose CPU, memory, hard disk and other components can be upgraded or replaced as needed. Motion control is realized through external PCIe cards, Ethernet cards or USB cards.
Powerful Computing and Graphics Processing Capabilities
Benefiting from the performance of modern PC hardware, the system can easily process complex 3D models, perform a large number of tool path calculations and real-time 3D graphics simulation—an advantage unmatched by many closed embedded systems.
Rich and Flexible Human-Computer Interaction
Operation is conducted via standard large-size displays, keyboards and mice, with highly intuitive file management and parameter setting. Users can easily connect peripheral devices such as network, USB flash drives and handwheels.
Highly Scalable Functions
Functions can be infinitely expanded through software plug-ins or secondary development, such as supporting more axes, connecting robots, integrating vision systems, and customizing exclusive process modules.
⚠️ Disadvantages
System Stability Challenges
- Real-time performance defects: Standard Windows/Linux are not real-time operating systems, which may have timing jitter under high requirements and risk step loss. Although this can be mitigated by hardware control cards, the root cause remains.
- System complexity: Background programs running on the PC, driver conflicts, viruses or Windows updates may cause software crashes or machining interruptions, posing risks to the production environment.
- Poor environmental tolerance: Ordinary PCs are not resistant to dust, vibration and high temperature/humidity in workshop environments, requiring additional protection.
High Requirements for Users
Users need to have a certain level of computer and CNC knowledge to complete system installation, optimization, maintenance and troubleshooting. It is not an out-of-the-box solution.
Potentially High Total Cost of Ownership
Pursuing industrial-grade stability requires investment in industrial PCs, high-quality motion control cards, genuine software and continuous maintenance efforts.
2. Embedded All-in-One Control Systems
The embedded all-in-one control system for CNC Routers is a dedicated control device that highly integrates a computer, motion controller, human-machine interface (HMI) and I/O interfaces into a single professional industrial enclosure. It is not a general-purpose computer, but a dedicated one built exclusively for the single task of controlling CNC Router Machines.

The SYNTEC 60WE series CNC system
✅ Advantages
High Integration & Machine-Specific Design
- Hardware integration: The computing unit (CPU), motion control core (FPGA/dedicated chip), HMI (touch screen), I/O interfaces, power supply and other components are physically integrated into a rugged industrial enclosure, with no separate parts or redundant cables.
- Software-hardware unification: Proprietary software is deeply integrated with hardware and fully optimized as a whole before delivery, ensuring optimal performance and stability.
Hard Real-Time Response
- Deterministic response: Motion control tasks are processed directly by hardware (e.g., FPGA), delivering microsecond-level determinism and ultra-high reliability.
- Fast interrupt response: Extremely quick response to safety signals such as emergency stop and limit switches, ensuring operational safety.
Ultra-Simplified Operation
- Out-of-the-box usability: The machining interface loads quickly after power-on, with no need to boot a general-purpose operating system.
- Task-specific interface: All buttons and menus are custom-designed for machining, featuring a simple and intuitive logic that drastically reduces learning costs and misoperation rates.
Strong Environmental Adaptability
- Robust and durable: Typically designed with dust and vibration resistance, and equipped with wide-temperature components, it can withstand harsh industrial environments with dust, oil contamination, vibration and electromagnetic interference.
- Long-term stability: Boasts a high mean time between failures (MTBF), ideal for 24/7 continuous production.
Defined Product Lifecycle
- Long-term availability: Fixed hardware platform and software version ensure long-term supply and compatibility.
- Predictable costs: Clear maintenance and upgrade paths (vendor-dependent), making the total cost of ownership (TCO) easy to calculate.
⚠️ Disadvantages
Highly Closed System
It runs a deeply customized embedded operating system (e.g., Linux RT). Users cannot install any third-party software and can only use the functions preconfigured by the manufacturer.
Long-Term Vendor Lock-in
Once a brand is selected, subsequent maintenance, spare parts supply and process upgrades are subject to the manufacturer's service system and business strategies.
Performance Bottlenecks
Its computing power is fixed by the factory-fitted ARM or low-power x86 chip. When processing complex 3D relief models (with millions of faces), its computing speed is significantly slower than that of high-performance PCs of the same generation.
3. Embedded Handheld Controller Systems
An embedded handheld controller system is a fully self-contained CNC motion controller. It integrates a processor, motion control chip, storage unit and operating interface internally, and controls the machine tool directly by connecting to drivers. Its market positioning is to achieve an ultimate balance between stability and cost, pursuing ultra-simplified operation and complete offline working.
Similar to an embedded all-in-one system, the handheld controller system features a smaller screen (mostly LCD) and its functions are more focused on execution rather than editing, with relatively simplified functionality overall.
This system typically adopts a high-performance DSP or ARM chip as the main processor, responsible for G-code parsing and logic control; it also integrates an FPGA or dedicated IC to generate high-precision pulses. Users operate via a handheld control panel (handheld controller), which usually includes a main control board, buttons, an LCD screen, USB ports and other components.
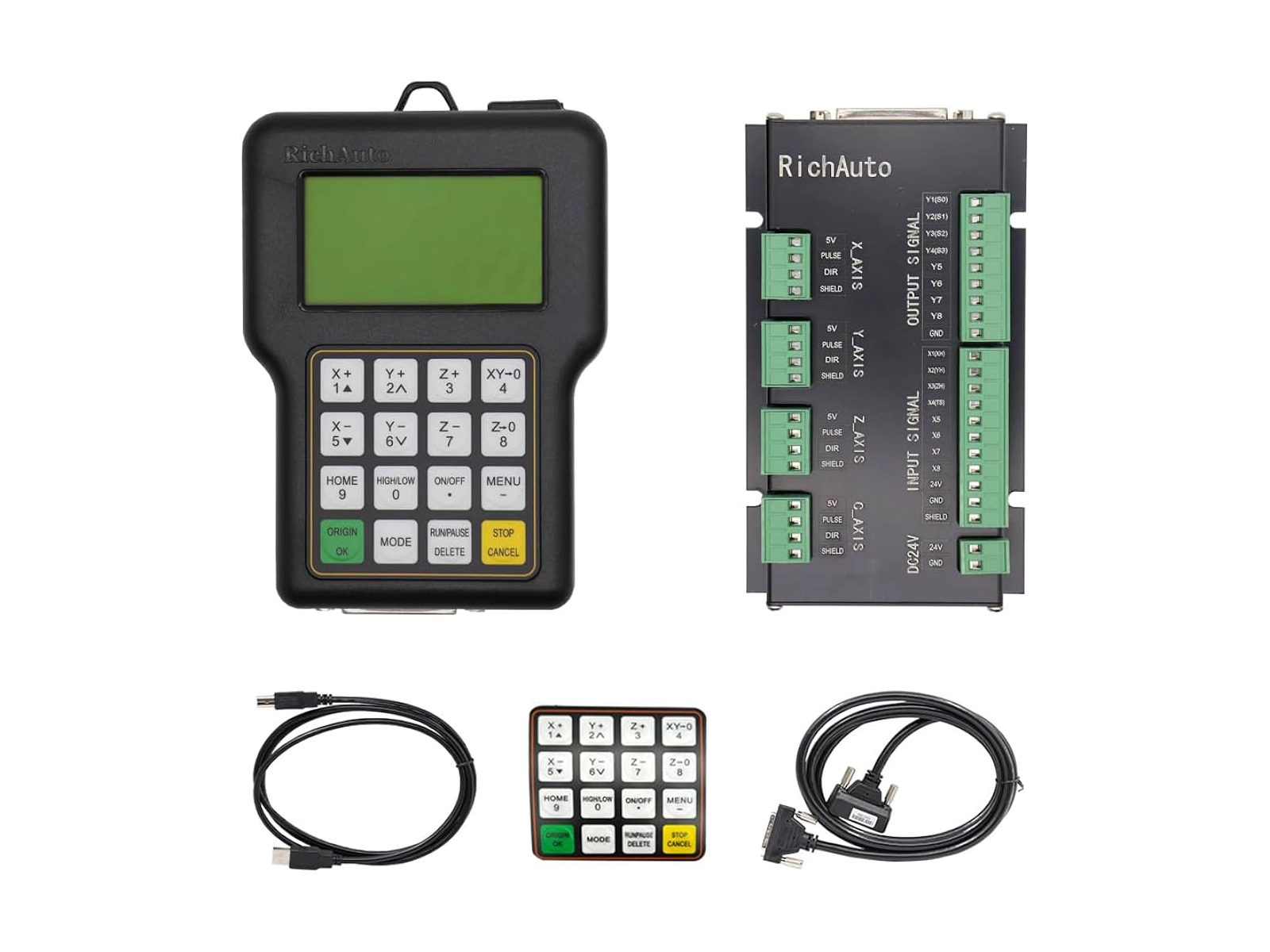

The RichAuto A1X series DSP control handles
✅ Advantages
Ultimate Stability and Reliability
- Fully offline operation, completely free from the impacts of computer viruses, system crashes and freezes.
- Motion control is directly guaranteed by hardware circuits, with no risk of step loss.
Ultra-low Cost
It eliminates the costs of industrial PCs, displays and other components, making it one of the most cost-effective CNC solutions available.
Simple Operation and Easy Maintenance
- Clearly marked function buttons with an extremely low learning threshold.
- The closed system requires almost no software maintenance.
- Compact size for easy installation and replacement.
Exceptionally Strong Environmental Adaptability
- Low power consumption and minimal heat generation, adaptable to high-temperature and high-dust workshops.
- Connected to the cabinet via a flexible cable, allowing users to hold the device and monitor machining in real time.
⚠️ Disadvantages
Relatively Single Functionality
It usually only has core motion control functions (G-code execution, I/O control).
Poor Human-Computer Interaction Experience
- The small-size LCD screen (often monochrome) has limited information display capability.
- Reliance on physical button operation makes parameter setting and viewing less intuitive and efficient than touch screen operation.
Limited File Processing Capability
- There are strict restrictions on the size and complexity of machining program files, making it unable to process ultra-large files.
- It usually only supports standard G-codes, and may have poor compatibility with special codes generated by some CAM software.
Almost Zero Scalability and Upgradability
- Functions are fixed at the factory, and users cannot add any new features.
- Upgrades are completely dependent on firmware versions released by the manufacturer, with extremely limited upgrade space.
What CNC Systems for CNC Routers?
Based on the three major categories above, we have compiled the commonly used CNC systems for CNC routers for you:
1. PC-based Systems
1) Mach3 / Mach4
Features: The most renowned entry-level commercial software for the Windows platform. Mach3 boasts a robust ecosystem but an outdated kernel; Mach4 is more modern yet with an immature ecosystem. Must be used with a parallel port card or USB/Ethernet motion control card.
Positioning: Ideal for hobbyists, small workshops and low-cost entry-level applications. A popular choice for learning CNC fundamentals.
2) Weihong (NcStudio)
Features: A commercial system with an extremely high market share in China's router industry. The software runs on Windows systems, the software is encrypted and bound to the brand's own PCIe/Ethernet control cards, optimized for engraving with excellent stability.
Positioning: A standard production tool for small and medium-sized advertising, woodworking and stone processing workshops.
3) XDW
Features: Widely applied in multi-functional CNC routers, supporting oscillating tools and CCD vision systems.
Positioning: Commonly used in multi-functional CNC routers equipped with oscillating tools.
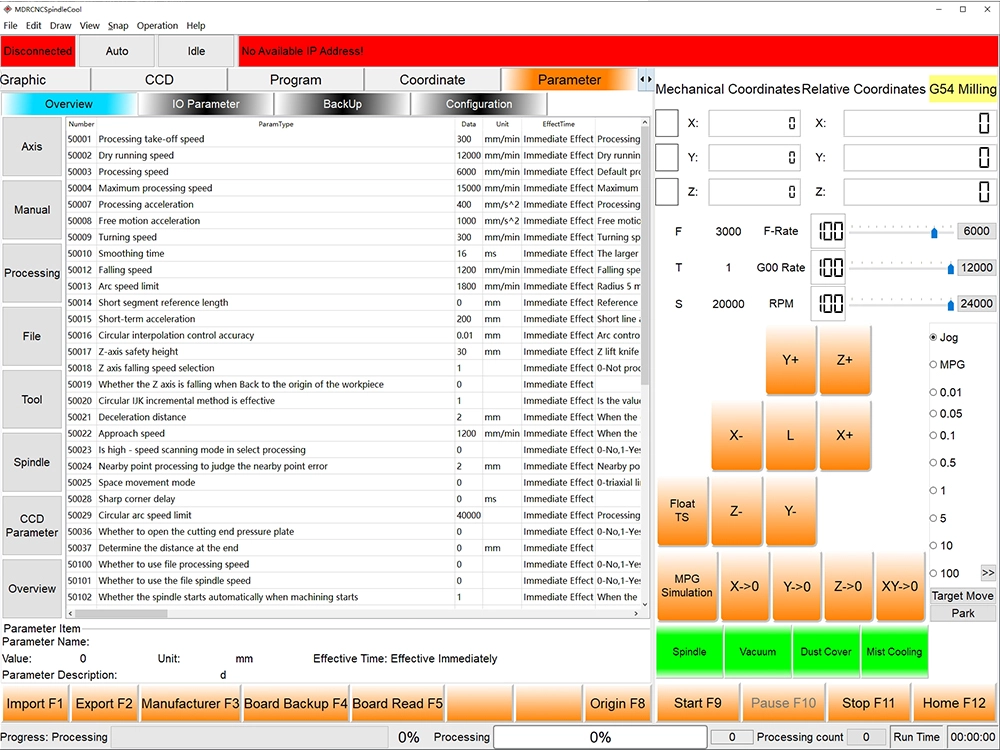
2. Embedded All-in-one Control Systems
1) LNC
Features: A Taiwanese system with stable performance and an intuitive human-machine interface. It has an excellent reputation for long-time high-load machining and high-speed, high-precision performance, with a more "structured" system architecture and superior multi-axis control capabilities.
Positioning: Widely used in ATC CNC routers, multi-axis CNC routers and multi-functional CNC lathes.
LNC MW2600D (External keyboard, mouse, and monitor are required.)

LNC MW5800
2) Syntec
Features: A Taiwanese CNC system with high international acceptance, renowned for its solid control kernel and stability. Commonly seen in woodworking and stone processing centers with highly targeted functions.
Positioning: Widely applied in ATC CNC wood routers, small CNC metal milling machines and CNC stone routers.
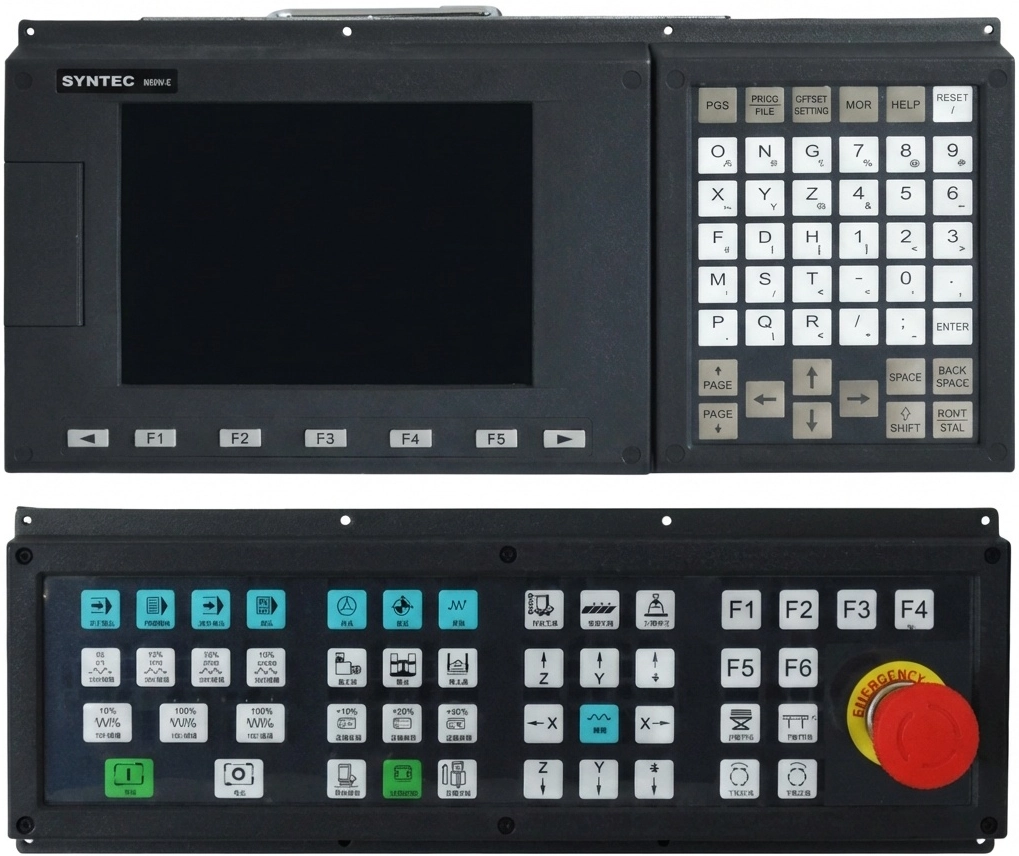

Syntec 60WE
3) Siemens
Features: A benchmark for industrial-grade reliability, with unparalleled stability and durability, easily handling complex 5-axis machining scenarios.
Positioning: For high-end precision manufacturing where excellence and reliability are pursued regardless of cost. Mainly used in high-value-added precision mold, aerospace component and automotive mold processing centers (high-end woodworking or composite material processing), rather than ordinary woodworking engraving.
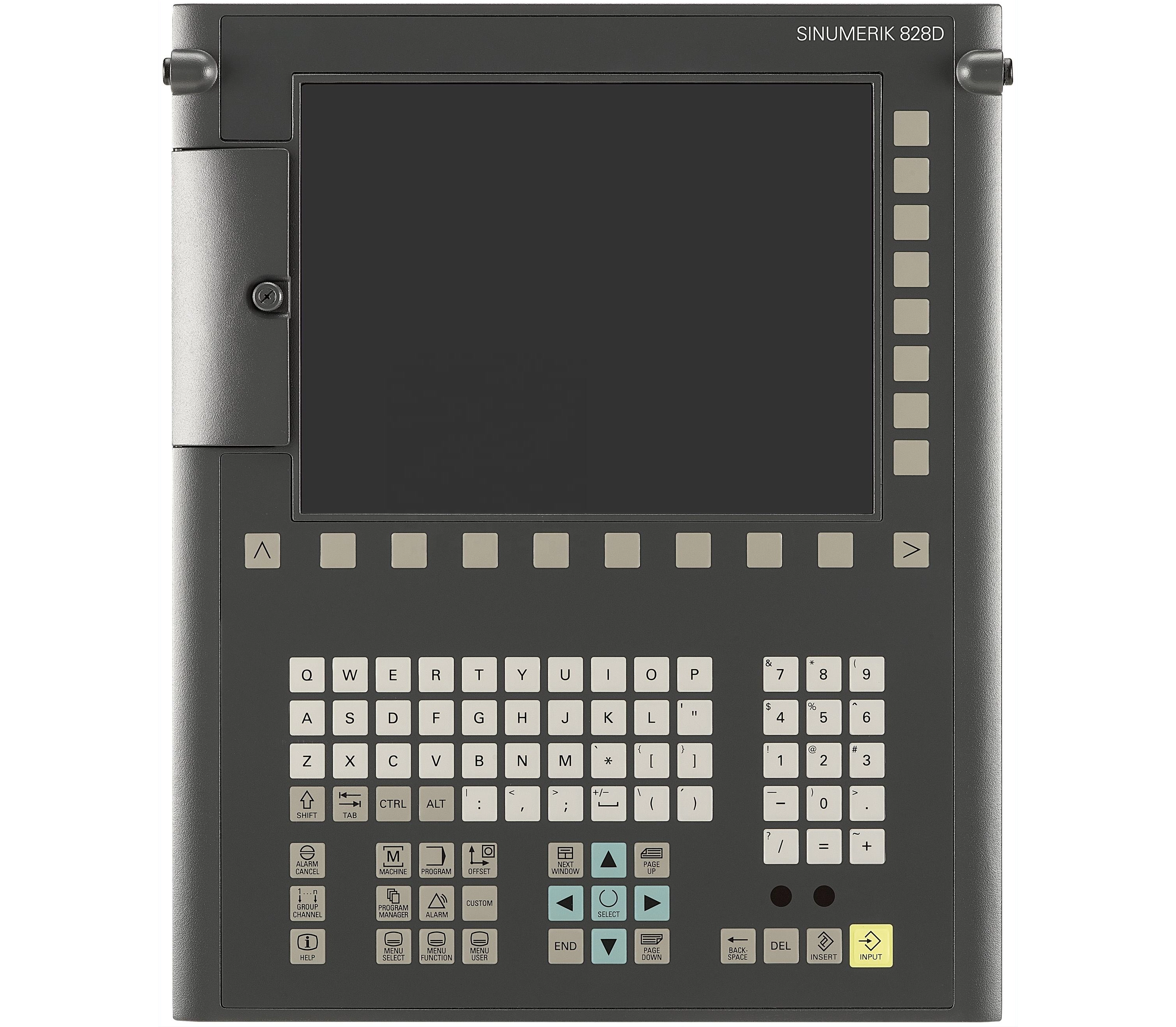

Siemen SINUMERIK 828D
4) FANUC
Features: Equally famous as Siemens. Its Series 0𝑖-MODEL F and other series are highly integrated high-end all-in-one control systems, renowned for zero failure performance yet with a relatively high price tag.
Positioning: Suitable for industrial production lines requiring mass production and ultra-high reliability.
FANUC 0𝑖-TF Plus
3. Embedded Handheld Controller Systems
1) RichAuto
Features: The RichAuto DSP handheld controller is one of the most representative offline controllers with an extremely high market share in the current CNC wood router market,. It offers unbeatable cost performance and popularity, with all basic core functions of a DSP controller: G-code execution, manual operation (jog, step, continuous), tool setting, machining origin setup, speed adjustment, etc.
Certain models of this control handle supports 3D tool path preview (displayed as line graphics on a simple LCD screen) – a highly practical feature for users, superior to early controllers with pure text display.
It boasts an extremely diverse product line that covers the low, medium and high-end market segments, with each product series varying in appearance and functionality. For instance, its A1X Series is commonly used for cost-effective standard 3-axis CNC routers or 4-axis CNC routers; the B4X Series is typically applied to ATC CNC routers; and the B5X Series is typically applied to multi-station CNC wood routers. Each of these series is further subdivided into multiple models, with the specific selection to be determined by the user's actual needs.
Positioning: Its DSP control handles are compatible with most types of CNC routers – ranging from 3-axis to 4-axis models, from standard CNC routers to ATC CNC routers, and from CNC wood routers to CNC stone routers. The high-end series of this control handle is even priced on par with certain all-in-one embedded systems.
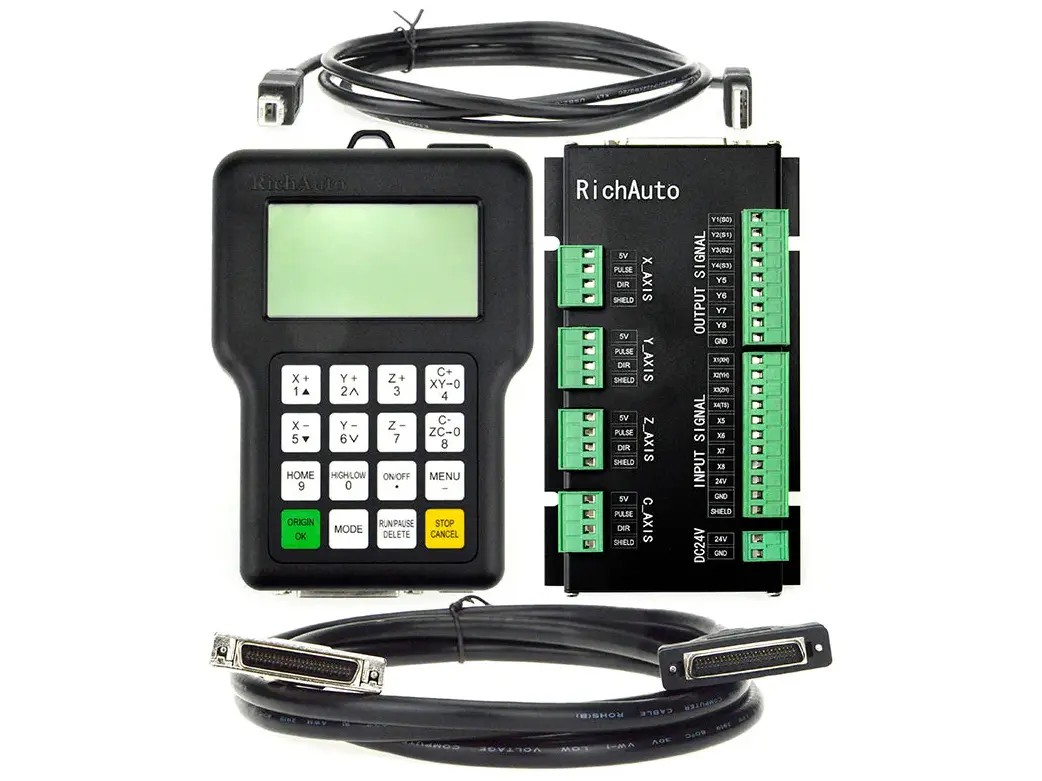

RichAuto A11 DSP handle
RichAuto B4X DSP handle
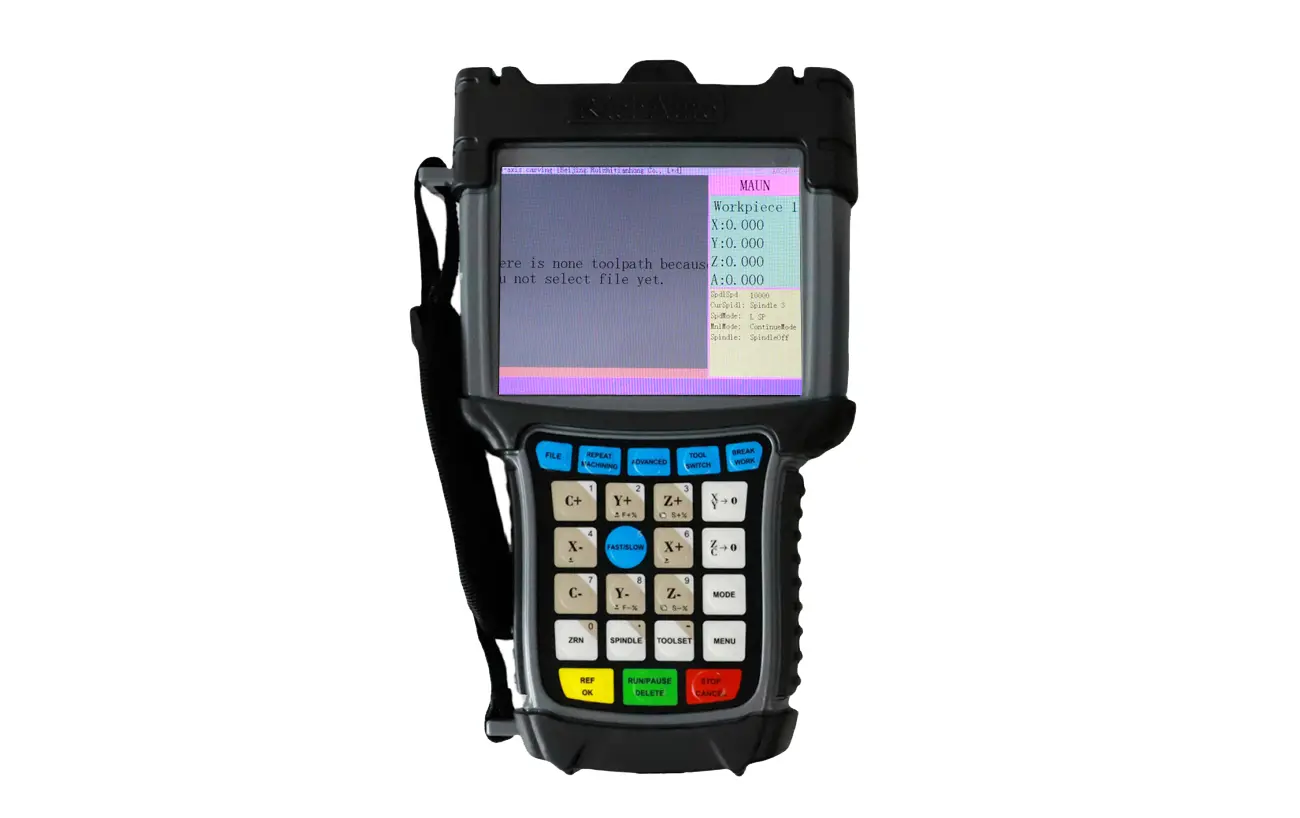

RichAuto B5X DSP handle
2) Weihong
Features: Weihong's NK105 series handheld control system is also a common choice in the industry, supporting standard 3-axis or 4-axis engraving and milling functions, and widely used in CNC wood lathes, CNC router machines, CNC plasma cutters and other machine.
Positioning: For single-function CNC wood routers or those with ultra-budget requirements, mainly used in 3-axis or 4-axis CNC routers.
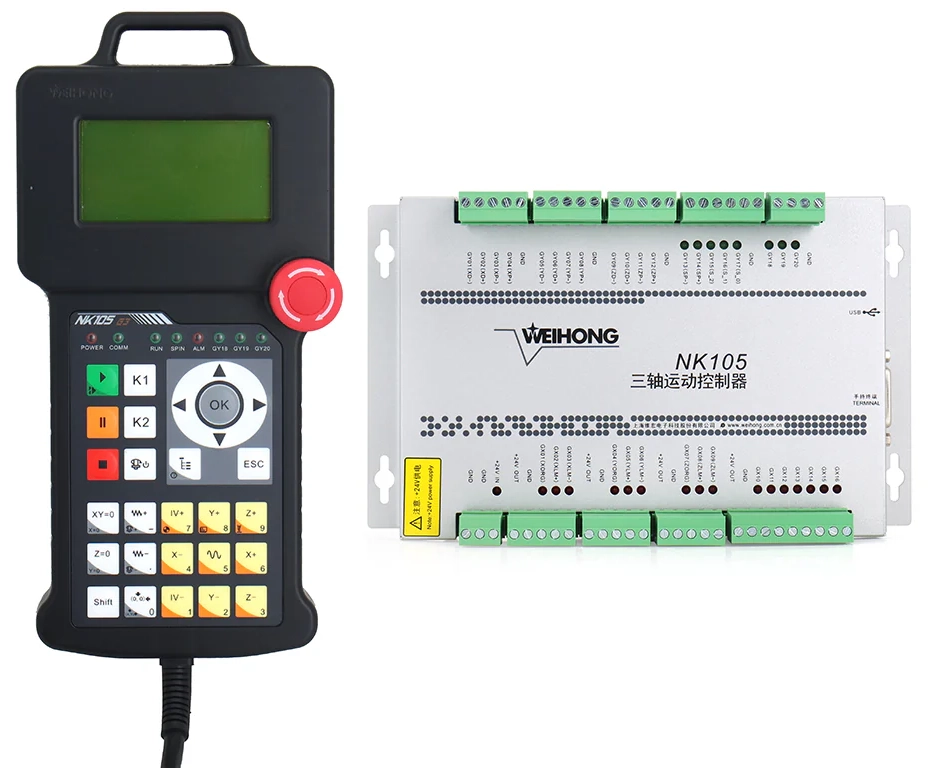
Weihong NK105 DSP handler
How to Choose the Right Control System for a CNC Router?
hen choosing a control system for a CNC Router, there is no absolutely perfect option—only the one that best aligns with your actual needs, budget and technical capabilities. Here are three guiding principles for reference:
Demand-driven, Not Price-driven
Paying for unnecessary functions is a waste, yet sacrificing critical stability to save a few thousand dollars will result in far greater subsequent losses.
Stability Above All Else
For production operations, uninterrupted running is ten times more important than a rich set of functions.
The Matching Principle
The grade of the control system should match that of the machine's main body (mechanical structure and drive motors). A top-tier system is meaningless when installed on an underconfigured machine.
Please answer the following questions to find out the most suitable control system for you:
Evaluation results
Most suitable system: DSP offline handheld controller systems (e.g., RichAuto).
Explanation:These systems solve the "from zero to one" problem at the lowest cost, with intuitive operation and no PC maintenance required. Though limited in functions and cumbersome for file processing, they are fully capable of completing basic cutting and engraving tasks. The high-end control panels can even deliver performance on par with all-in-one embedded systems, with the only difference lying in their form factor of use.
Most suitable system: PC-based systems, mid-range embedded all-in-one control systems (e.g., Weihong, LNC, Syntec)
Explanation:This is the mainstream choice in the market, striking the optimal balance between stability, ease of use and functionality. With powerful features and intuitive operation, these systems handle the vast majority of commercial orders, withstand harsh workshop conditions and support continuous operation—delivering the highest return on investment.
Most suitable system: Top-tier industrial all-in-one control systems (e.g., Syntec EzMotion, Siemens 828D)
Explanation:Only these systems can deliver the high-speed processing power, ultra-high precision control and advanced functions required for complex curved surface calculation. Built as professional production tools, they come with a premium price tag but are indispensable for high-end machining.
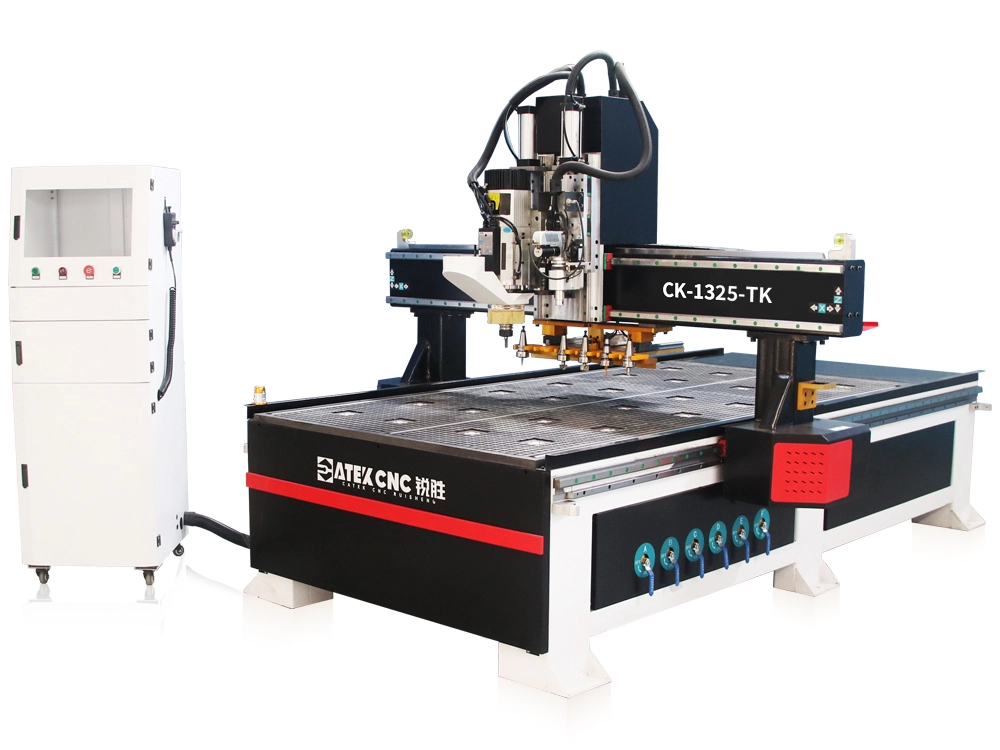
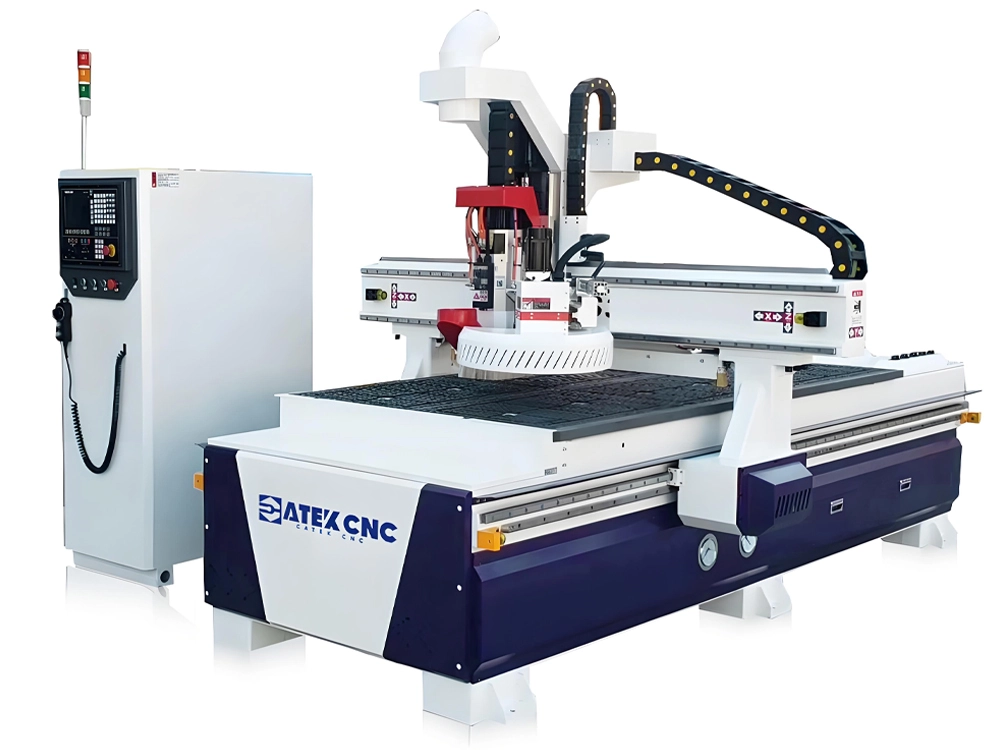
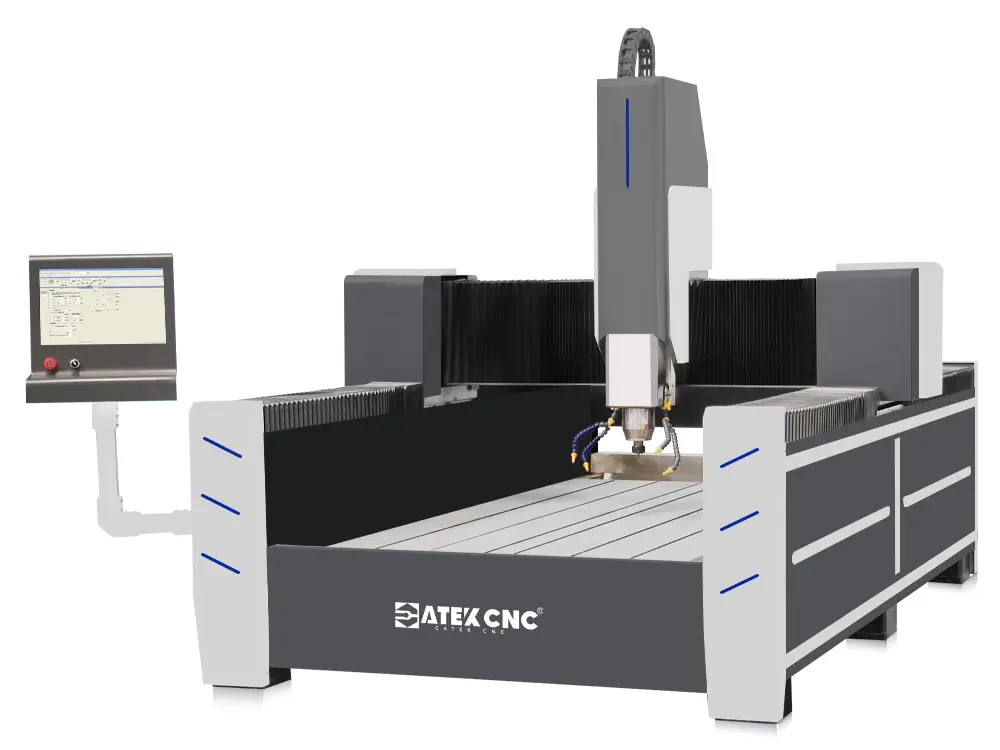
RELATED MODELS
We recommend some related models for you...





